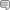 0
comments
|
Tuesday, April 15, 2008
0
comments
|
Tuesday, April 15, 2008
 The circulatory system is the system of transporting the body. It is composed of a group of bodies that carry blood throughout the body. The heart pumps blood in the arteries and veins of transportation. Blood oxygen-rich leaves the left side of the heart and spends most artery, called the aorta. The aorta branches in small arteries, which at the same branch smaller vessels that travel throughout the body. When blood enters the smallest blood vessels, called capillaries, and can be found in the tissues, it provides nutrients and oxygen to cells, and takes into carbon dioxide, water and waste. The blood, which contains more oxygen and nutrients, and then goes back to the heart through the veins. Veins carry waste out of blood cells and to bring back to heart, which pumps it to the lungs to take in oxygen and remove waste carbon dioxide.
The circulatory system is the system of transporting the body. It is composed of a group of bodies that carry blood throughout the body. The heart pumps blood in the arteries and veins of transportation. Blood oxygen-rich leaves the left side of the heart and spends most artery, called the aorta. The aorta branches in small arteries, which at the same branch smaller vessels that travel throughout the body. When blood enters the smallest blood vessels, called capillaries, and can be found in the tissues, it provides nutrients and oxygen to cells, and takes into carbon dioxide, water and waste. The blood, which contains more oxygen and nutrients, and then goes back to the heart through the veins. Veins carry waste out of blood cells and to bring back to heart, which pumps it to the lungs to take in oxygen and remove waste carbon dioxide.Blood Flows in this order:
- The superior (a) and inferior (b) vena cava are the main veins that receive blood from the body. The superior vena cava drains the head and arms, and the inferior vena cava drains the lower body.
- The right atrium receives blood from the body via the vena cavae. The atria are on the top in the heart.
- The blood then passes through the right atrioventricular valve, which is forced shut when the ventricles contract, preventing blood from reentering the atrium.
- The blood goes into the right ventricle (note that it has a thinner wall; it only pumps to lungs). The ventricles are on the bottom of the heart.
- The right semilunar valve marks the beginning of the artery. Again, it is supposed to close to prevent blood from flowing back into the ventricle.
- The pulmonary artery or pulmonary trunk is the main artery taking deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
- Blood goes to the right and left lungs, where capillaries are in close contact with the thin-walled alveoli so the blood can release CO2 and pick up O2.
- From the lungs, the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood back into the heart.
- The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
- The blood passes through the left atrioventricular valve.
- The blood enters the left ventricle. Note the thickened wall; the left ventricle must pump blood throughout the whole body.
- The blood passes through the left semilunar valve at the beginning of the aorta.
- The aorta is the main artery to the body. One of the first arteries to branch off is the coronary artery, which supplies blood to the heart muscle itself so it can pump. The coronary artery goes around the heart like a crown. A blockage of the coronary artery or one of its branches is very serious because this can cause portions of the heart to die if they don’t get nutrients and oxygen. This is a coronary heart attack. From the capillaries in the heart muscle, the blood flows back through the coronary vein, which lies on top of the artery.
- The aorta divides into arteries to distribute blood to the body.
- Small arteries are called arterioles.
- The smallest vessels are the capillaries.
- These join again to form venules, the smallest of the veins.
- These, in turn, join to form the larger veins, which carry the blood back to the superior and inferior vena cava.
Labels: Circulatory System, Systems of the Body


0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home